Ether.Genius
 Ether.Genius is a handheld tester 100% suitable for labs or field use because is full equipped (IP/Ethernet/PTP/T1/E1), battery operated (up to 24h of operation), light (1.1kg) and very rugged. The unit is able to test Ethernet/IP networks up to 1Gb/s while supporting master/slave Sync-E/PTP emulation. It also has interfaces for PDH/T1/E1/E0 and IEEE C37.94. Operation modes includes Performance, Quality and Wander tests at all interfaces and the ability to emulate and analyse PTP/SyncE, while measuring Freq./Phase, PDV metrics, analyse/generate TIE/MTIE/TDEV and TE. A built-in Rubidium clock disciplined with GPS provides an accuracy of a few nsec.
Ether.Genius is a handheld tester 100% suitable for labs or field use because is full equipped (IP/Ethernet/PTP/T1/E1), battery operated (up to 24h of operation), light (1.1kg) and very rugged. The unit is able to test Ethernet/IP networks up to 1Gb/s while supporting master/slave Sync-E/PTP emulation. It also has interfaces for PDH/T1/E1/E0 and IEEE C37.94. Operation modes includes Performance, Quality and Wander tests at all interfaces and the ability to emulate and analyse PTP/SyncE, while measuring Freq./Phase, PDV metrics, analyse/generate TIE/MTIE/TDEV and TE. A built-in Rubidium clock disciplined with GPS provides an accuracy of a few nsec.
You may buy just a last generation dual port 1GbE tester and then you may add other interfaces just when you need it by a simple and easy upgrade by code. Then you will be able to get the new firmware supporting the desired functionalities.
Platform
Multiport Interfaces
- A:B ports: 2 x SFP (100MbE, 1GbE)
- A:B ports: 2 x RJ45 (10MbE, 100MbE, 1GbE)
- C:D ports: Balanced 2 x RJ45 (T1/E1)
- C:D ports: Unbalanced 2 x BNC (T1/E1)
- DTE/DCE ports: V.35, V.24 / RS 232, V.11 / X.21, V.36, RS:530
- GNSS Port: SMA female
- PPS Ports: 3xSMA female (i/o)
Operation / Results
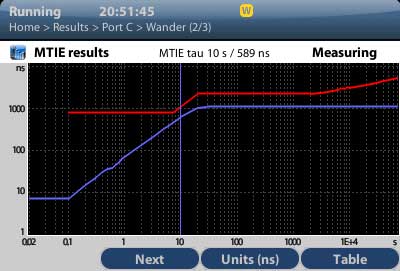
- Graphical results MTIE and TDEV
- Navigation: by touch screen, keyboard, mouse
- Remote Control: by VNC
- Storage capacity: one week of results
- Export: results in pdf/txt/csv through USB interface or SD card
- Report export to remote host through Ethernet / IP
Ergonomics
- Protection: shock-proof and rubber boot
- Light and easy to carry (weight: 1.2 kg)
- Start: Manual / Timed with optional password
- T1/E1 operation time = t > 24h
- GbE operation time = t > 12h
- 10GbE operation time = t > 6h (Ether10.Genius)
Batteries
Time / Clocks
Internal Clocks
- Default better than ±2.0 ppm
- OCXO better than ±0.1 ppm
- Rubidium better than ±5.0e-11 (GPS disciplined, warm- up: 600s)
Internal Rubidium clock
- Freq. accuracy (7.5 minutes warm up): ± e-9
- Freq. accuracy on shipment (24 h. warm up): ±5.0e-11
- Aging (1 day, 24 hours warm up): ±0.5e-11
- Aging (1 year): ±1e-9
- Time accuracy (24 h. locked): ±50 ns
- Freq. accuracy: 1.5e-11 / 24h
- Time accuracy: ±100 ns / 2h, ±1.0μs / 24 h
Free―run (No GPS)
GPS locked
Hold - over (after 24 h. locked)
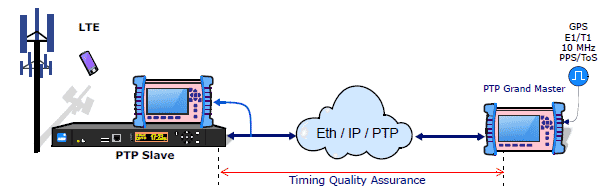
Input Clock References
- Rates: 1.544 Mb/s, 2.048 Mb/s, 1.544 MHz, 2.048 MHz, 10 MHz
- Built-in GPS receiver, 1 pps
- SyncE
Output Clock
- 1.544 MHz, 2.048 MHz, 10 MHz
- 1 pps
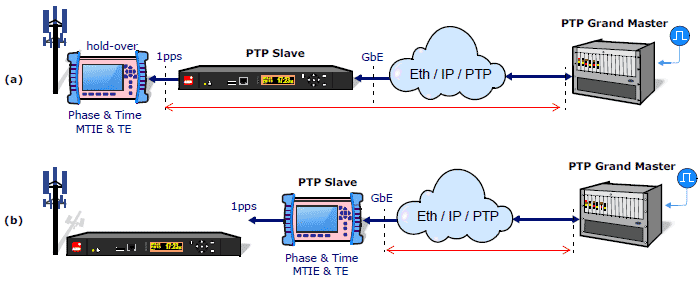
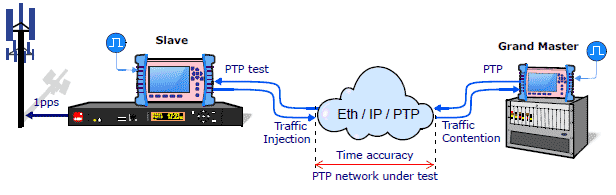
SyncE and PTP testing
- PTP profiles: Telecom and Power
- Encapsulations: Ethernet and UDP
- Clock emulation: Master / Slave, Unicast/Multicast, 128 packet/s
- PDV capture, protocol analysis and correction field support
Ethernet PTP Frequency testing
- Floor Delay Population (G.8260): FPC, FPR, FPP
- Wander: Analysis and Generation TIE, MTIE and TDEV (in real time)
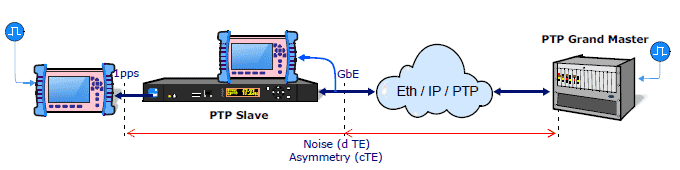
Ethernet PTP Phase testing
- Measured at GbE and 1pps interfaces
- Time Error (TE): Maximum (max |TE|), Dynamic (dTE), Constant Time Error (cTE)
1 pps testing
- Jitter
- Wander: TIE, MTIE, TDEV
- Time Error (TE): Maximum (max |TE|), Dynamic (dTE), Constant Time Error (cTE)
Synchronous Ethernet
- ESMC / SSM: Generation, decoding and transparent forwarding
- Wander: Analysis/Generation: TIE, MTIE and TDEV (in real time)
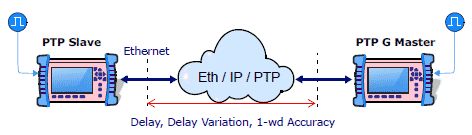
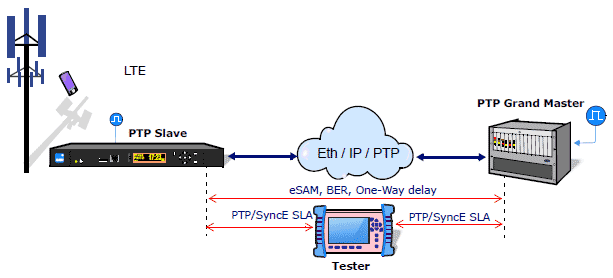
Latency/Delay measurements
Datacom, C37.94, E1, T1, and 1GbE interfaces
- Round-trip delay (RTD)
- One-way delay (OWD) GPS assisted
Ethernet PTP (GbE)
- Path delay asymmetry
- End-to-end / peer-to-peer path delay mechanisms
- Master-to-slave / Slave-to-grandmaster latency
- PTP packet delay variation test
Ethernet/IP Testing
8 x independent streams
- Streams: may use individual sour/dest. addresses and bandwidth profile
- Internet Protocol: IPv4 / IPv6 support
- Frames: DIX, VLAN, Q-in-Q, CoS (DSCP/PCP), MPLS, and Jumbo
- IP with UDP or arbitrary protocol
- DHCP for source IP and ARP for destination MAC
Counts et statistics
- Frame counts, IP traffic statistics, and bit rate
- Top ten VLAN, MAC, IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
- QoS: Latency, Delay variation, Loss ratio, SES, Availability, Out-of-Sequence, Duplicated
BER Tests et Patterns
- Traffic generation: Continuous, Burst, Ramp, Random
- PHY layer: RPAT, JPAT, SPAT, HFPAT, LFPAT, MFPAT, LCRPAT, SCRPAT
- Layer 2/4 PRBS: 2e11-1, 2e15-1, 2e20-1, 2e23-1, 2e31-1
- Layer 2/4 PRBS: all inverted versions
Symmetric/Asymmetric RFC-2544
- Throughput
- Latency
- Loss
- Back-to-back
- System Recovery
Symmetric/Asymmetric eSAM (Y.1564)
- Latency, Delay Variation, Loss, and Availability
- Eight / four services (colour/not colour)
- CIR, EIR, max, Througput
Loopback
- L1 - L4 loopback mode
- Traffic filtering by
- sour/dest MAC/IP/Port
- VLAN, CoS (DSCP/PCP)
- Protocol
PDH / T.Carrier testing
- T1 (ANSI T1.102)
- E1 (ITU-T G.703)
- E0/Co-Directional (ITU-T G.703)
- Terminal
- Monitor
- High Impedance
- Pass-through
- T1: Framed SF and ESF and unframed Generation/Analysis
- E1: Framed PCM-30 / 31 with/without CRC and Unframed signals
- T1/E1: Display and Edition: all fields, CAS, Pulse Masks, Events
- Channel map: Busy/Free, External Drop/Insert of 64 kb/s co-dir or datacom
- BER
- Line/Freq
- Errors/Alarms
- G.821, G.826, M.2100
- VF: tone generation/analysis
- Attenuation, Freq, Freq. deviation, Level, Peak codes
- Jitter analysis: Peak to peak, RMS, hits, count (0.1 to 100 kHz range)
- Wander: Analysis/Generation and masks (1 μHz to 10 Hz range)
- Wander Analysis/Generation in 10 MHz, 2048 kHz, 1544 kHz, 1pps
Interfaces
Modes
Measurements
Synchronization
C37.94 testing
C37.94 SFPs
Operation Modes
Analysis & Generation
Delay & Freq. Tests
Cable features
- Wiremap
- Skew
- Cable Diagnostics
- Distance to fault
Power over Ethernet
- PoE and PoE+
- Volts / Current
Cable tests
Datacom testing
- Terminal emulation
- Bi-directional Monitoring
- Datacom / E1 mux
- DTE/DCE control circuit
- Timing circuits
- Binary rates
- BER, Frequency
- Insertion/Analysis of events
- G.821
Modes
Display and Edition
Tests